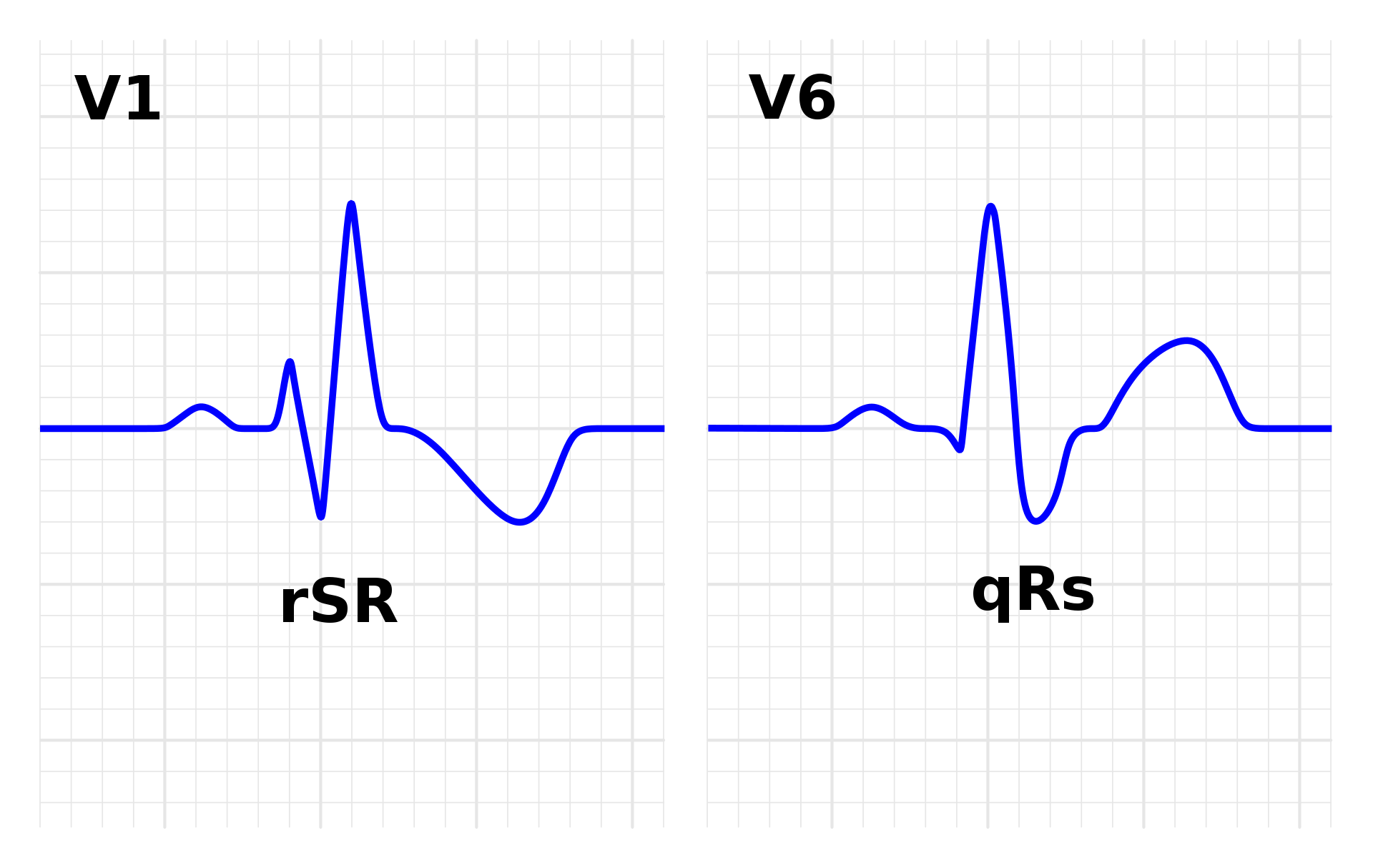
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular Tachycardia Introduction Tachycardia refers to a heart rate >100 beats per minute (bpm). The tachycardia may be supraventricular or ventricular depending on the origin of the arrhythmia. Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): If the tachycardia originates above the bifurcation of the bundle of His, usually in the atria or atrioventricular (AV) junction, the tachycardia is supraventricular. …